This article examines 11 Hepatitis B Symptoms and 3 treatment strategies. Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the liver and can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Understanding the Hepatitis B Symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management of the disease. In this article, we will explore the various symptoms associated with Hepatitis B, how they manifest, and what you can do if you suspect you have been infected.

Table of Contents
What is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV), which is transmitted through contact with infectious body fluids, such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions. The virus can lead to both acute and chronic liver diseases, with chronic infections potentially resulting in liver cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Modes of Transmission
Understanding how Hepatitis B spreads is essential for prevention. The primary modes of transmission include:
- Unprotected Sexual Contact: Engaging in sexual activities without the use of protective measures, such as condoms, can significantly increase the risk of transmitting the virus to individuals. This lack of protection allows the exchange of bodily fluids, which may carry the virus, putting both partners at a higher risk for infection.
- Sharing Needles: Individuals who use intravenous drugs face an elevated risk of contracting the virus, particularly when they share needles or other paraphernalia associated with drug use. This practice creates a direct pathway for the virus to be transmitted between users, making it crucial to avoid sharing any equipment that may come into contact with blood.
- Mother to Child Transmission: Pregnant women who are infected with Hepatitis B have the potential to transmit the virus to their newborns during the process of childbirth. This vertical transmission can occur as the baby passes through the birth canal, highlighting the importance of monitoring and managing the health of pregnant women who are carriers of the virus to prevent infection in their infants.
- Blood Exposure: Healthcare workers and individuals who may come into contact with infected blood are also considered to be at significant risk. This includes situations where they are involved in medical procedures, providing emergency care, or handling contaminated materials, necessitating strict adherence to safety protocols to minimize potential exposure to the virus.
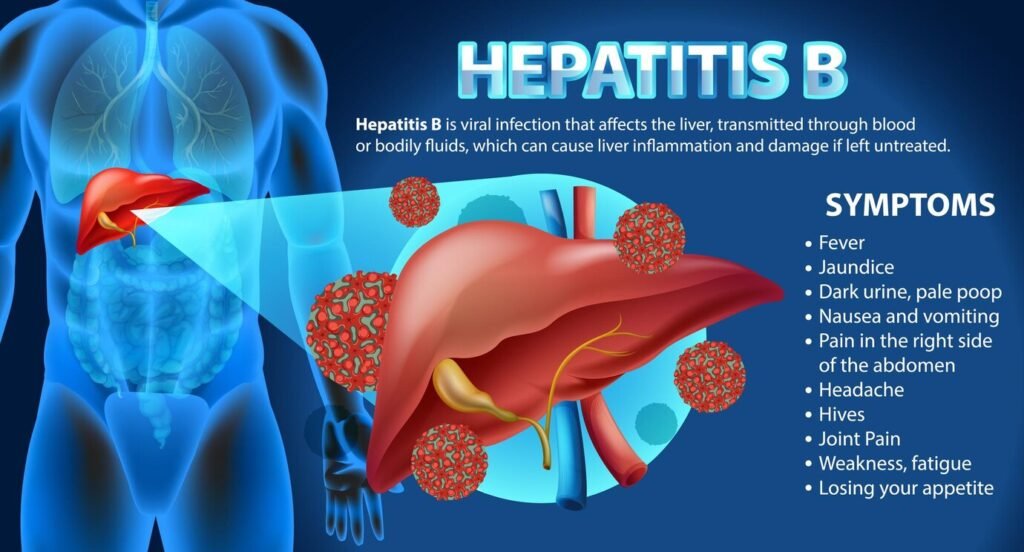
Early Hepatitis B Symptoms
In many cases, the Hepatitis B Symptoms may not appear until several weeks after infection. This period, known as the incubation period, typically ranges from 30 to 180 days. Early Hepatitis B Symptoms can resemble those of the flu and may include:
- Fatigue: This condition is characterized by a persistent and overwhelming sense of tiredness that remains constant and does not show any sign of improvement even after periods of rest or sleep. Individuals experiencing this symptom often find it difficult to carry out their daily activities due to an overwhelming lack of energy.
- Loss of Appetite: This symptom is marked by a noticeable and significant decrease in the desire or urge to eat. It can manifest as a disinterest in food that previously was enjoyed, leading to a reduction in food intake and potential nutritional deficiencies over time.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These Hepatitis B Symptoms involve a sensation of sickness that can often escalate to the point of inducing vomiting. Nausea is characterized by an uneasy feeling in the stomach, which may be accompanied by a strong urge to vomit, causing distress and discomfort.
- Abdominal Pain: Individuals may experience discomfort or pain localized in the upper right side of the abdomen, an area where the liver is situated. This type of pain can vary in intensity and may be indicative of underlying health issues, prompting further investigation into the individual’s condition.
- Joint Pain: This is described as unexplained or unexplained discomfort in the joints. Such pain can vary from mild to severe and may serve as an indication of an underlying infection or other medical conditions that warrant careful examination and consideration for appropriate treatment options.

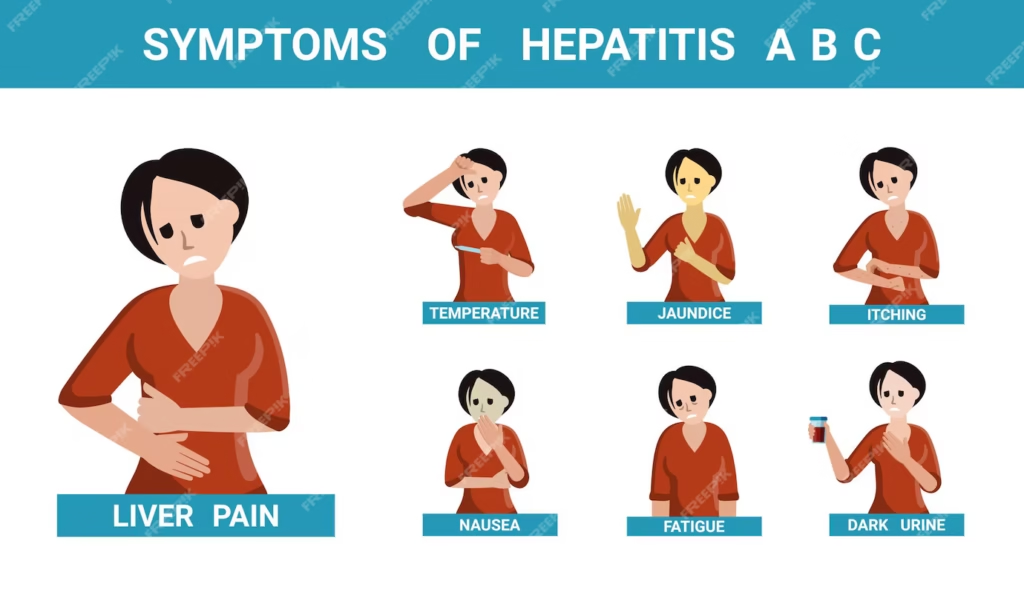
Acute Hepatitis B Symptoms
If the infection progresses to acute Hepatitis B, additional Hepatitis B Symptoms may develop, including:
- Jaundice: This condition is characterized by a noticeable yellowing of both the skin and the whites of the eyes, which occurs due to an accumulation of bilirubin in the bloodstream. The presence of excess bilirubin can be a sign of various underlying health issues, often related to liver dysfunction or biliary obstruction.
- Dark Urine: Individuals experiencing this symptom may notice that their urine appears darker than typical, often taking on shades that are reminiscent of tea or cola. This change in color is typically due to increased levels of bilirubin being excreted through the kidneys, indicating that there may be an imbalance in the body’s processing of this substance.
- Pale Stool: Another indication of potential health problems is the color of the stools, which may become significantly lighter than usual. This lightening of stool color is often a result of insufficient bile reaching the intestines, leading to a lack of the brown pigment that normally gives stools their characteristic hue.
- Itchy Skin: Additionally, a generalized itching sensation can occur throughout the body as a consequence of bile salts accumulating in the bloodstream. This itchiness, known as pruritus, can be quite uncomfortable and may be a key indicator of liver or biliary issues that warrant further investigation.
Why Early Detection Matters
Recognizing and diagnosing Hepatitis B at an early stage is incredibly important, as it plays a crucial role in preventing the disease from progressing to a chronic infection. The earlier the identification, the better the chances are for effective management and treatment. If you notice any of the Hepatitis B Symptoms associated with Hepatitis B, it becomes absolutely essential to seek the expertise of a healthcare professional who can provide you with the appropriate testing and diagnosis necessary for your health. Taking these steps can significantly impact your overall well-being and help mitigate the risks associated with this virus.
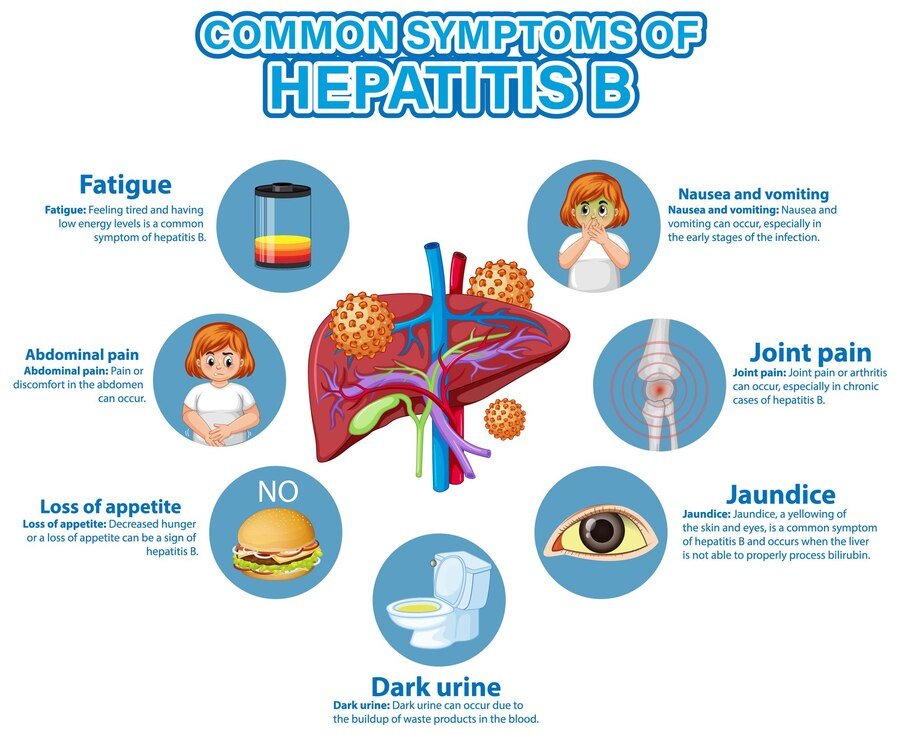
Chronic Hepatitis B Symptoms
For some individuals, Hepatitis B can become chronic, lasting six months or longer. Hepatitis B Symptoms may be mild, making identification difficult. However, possible Hepatitis B Symptoms include:
- Persistent Fatigue: This condition is characterized by a prolonged and ongoing sense of tiredness that significantly impacts an individual’s ability to carry out their daily activities and responsibilities. Individuals experiencing persistent fatigue may find it difficult to concentrate and may also feel a lack of energy, which can affect their overall quality of life.
- Abdominal Discomfort: This term refers to the presence of chronic pain or discomfort specifically located in the area of the liver. People with this discomfort may experience a constant dull ache or a sharp pain, which can be distressing and may warrant medical attention for further evaluation and management.
- Liver Damage Symptoms: These can manifest in various ways, including easy bruising, which indicates a potential issue with blood clotting. Additionally, swelling in the abdomen, known as ascites, can be another critical symptom, often resulting from fluid accumulation. Confusion that arises due to liver failure is also a significant Hepatitis B Symptoms, as it points to the liver’s impaired ability to detoxify the blood and regulate important metabolic processes.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring
Individuals diagnosed with chronic Hepatitis B should undergo regular monitoring to assess liver function and detect any Hepatitis B Symptoms of liver damage early. This proactive approach can help mitigate severe complications.
Diagnosis of Hepatitis B
The process of diagnosis generally includes conducting various blood tests that are aimed at determining if there are any Hepatitis B surface antigens (HBsAg) present in the bloodstream, alongside checking for the existence of specific antibodies and measuring the viral load. It is important to note that early and timely testing is vital for individuals who are identified as being at risk for infection, particularly in cases where Hepatitis B Symptoms may already be manifesting. Recognizing the importance of testing at an early stage can significantly influence health outcomes for those affected.
Common Diagnostic Tests
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test: This test is utilized to determine whether the Hepatitis B virus is currently present in the bloodstream. It is a crucial diagnostic tool that helps healthcare providers ascertain active infection and initiate appropriate management or treatment if necessary. The presence of the surface antigen indicates that the virus is replicating and that the individual is potentially infectious.
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test: This examination serves to indicate whether the body has successfully developed immunity to the Hepatitis B virus. It reflects the immune response following either a previous infection or vaccination against the virus. A positive result suggests that the individual is protected from Hepatitis B, reducing the risk of future infection.
- Hepatitis B Viral Load Test: This assessment measures the concentration of the Hepatitis B virus present in the blood. It plays a vital role in evaluating the severity of the infection and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment over time. By understanding the amount of viral load, healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding the management of the patient’s condition and determine the necessity for further interventions.
Treatment Options for Hepatitis B
While there is no cure for Hepatitis B, several treatment options are available to manage the infection and prevent complications:
- Antiviral Medications: Various antiviral drugs, including tenofovir and entecavir, play a crucial role in managing the Hepatitis B virus effectively. These medications can help to keep the viral load under control while simultaneously minimizing the damage inflicted on the liver over time. By adhering to a prescribed antiviral regimen, individuals can significantly improve their overall health outcomes and reduce the risks associated with chronic Hepatitis B.
- Regular Monitoring: For those living with chronic Hepatitis B, it is essential to undergo regular medical check-ups. These check-ups are vital for tracking the health of the liver and assessing any potential complications that may arise. Through consistent monitoring, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about treatment adjustments and ensure that any changes in liver function are detected early, thereby safeguarding the patient’s health.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making positive lifestyle modifications is another important aspect of supporting liver health for individuals with Hepatitis B. Embracing a nutritious diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can significantly benefit the liver. Additionally, avoiding alcohol consumption is crucial, as alcohol can exacerbate liver damage. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy weight through regular physical activity and balanced eating habits contributes to overall liver well-being and enhances the body’s ability to manage the virus effectively.
The Role of Vaccination
Vaccination is an effective preventive measure against Hepatitis B. The Hepatitis B vaccine is safe and can provide long-lasting immunity. It is recommended for infants, healthcare workers, and individuals at high risk of exposure.
Conclusion
Understanding the Hepatitis B Symptoms is essential for early detection and effective management of the disease. If you experience any of the Hepatitis B Symptoms discussed in this article, it is imperative to seek medical attention promptly. By being informed and proactive, you can take control of your health and reduce the risk of severe liver complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the first Hepatitis B Symptoms?
- The first signs may include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, and joint pain.
- How is Hepatitis B diagnosed?
- Diagnosis is typically made through blood tests that check for the presence of the virus and antibodies.
- Can Hepatitis B be cured?
- While there is no cure, antiviral medications can help manage the infection and prevent liver damage.
- Who should get vaccinated against Hepatitis B?
- The vaccine is recommended for infants, healthcare workers, and individuals at high risk of exposure.
- What lifestyle changes can help manage Hepatitis B?
- Maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding alcohol, and regular medical check-ups can support liver health.
By being aware of the Hepatitis B Symptoms and taking proactive measures, individuals can effectively manage Hepatitis B and lead healthy lives.


