This article covers the meningitis symptoms in adults. Meningitis is a serious medical condition that affects the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Understanding its symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. This article aims to provide a thorough overview of meningitis symptoms in adults, incorporating engaging content, actionable insights, and SEO optimization to ensure that it reaches those seeking information on this vital health topic.

Table of Contents
What is Meningitis?
Meningitis can be caused by various infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Bacterial meningitis is often more severe and can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly. Viral meningitis, while generally less severe, still requires attention. Recognizing the meningitis symptoms in adults early can be the key to effective treatment and recovery.
Common Meningitis Symptoms in Adults
Meningitis symptoms in adults can develop suddenly, often within hours or days. Here are the most common signs to watch for:
1. Fever and Chills
A high fever is considered one of the most distinct and recognizable meningitis symptoms in adults associated with meningitis. In most cases, this fever is usually accompanied by additional symptoms such as chills and sweating, which can further indicate the presence of this serious condition. If you or someone you are familiar with starts to experience a sudden and rapid onset of fever, it becomes crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Timely intervention is important in such situations, as meningitis can progress quickly and may lead to severe complications if not addressed adequately.
2. Severe Headache
A headache that is linked to meningitis is frequently characterized as being the most severe headache someone has ever felt in their lifetime. This overwhelming and intense pain can persist for an extended period and may prove unresponsive to typical over-the-counter pain relief medications. Individuals suffering from this type of headache often find that common analgesics do little to alleviate their discomfort, leaving them in a state of distress and seeking more effective treatment options. The relentless nature of the pain can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life.
3. Stiff Neck
Meningitis frequently leads to a noticeable stiffness in the neck area, which can result in significant discomfort or even render it impossible to bring the chin down to the chest. This particular symptom is highly indicative of meningitis, as it serves to differentiate this serious condition from other types of headaches that individuals might experience. The presence of neck stiffness is an important clinical sign that healthcare professionals consider when diagnosing the underlying cause of a patient’s meningitis symptoms in adults.

4. Sensitivity to Light
Photophobia, which is also referred to as sensitivity to light, is a prevalent symptom experienced by many individuals. This condition can make exposure to bright lights particularly uncomfortable, often leading to an increase in the severity of headaches. As a result, those affected by photophobia frequently find themselves seeking out darker environments as a means to alleviate their discomfort and avoid further aggravation of meningitis symptoms in adults. The desire to escape harsh lighting is a significant aspect of their daily lives, influencing their choices regarding social activities and public spaces.
5. Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting often occur alongside a severe headache and high fever, creating a distressing combination of meningitis symptoms in adults. This set of conditions can ultimately lead to dehydration, a serious complication that exacerbates the overall health situation and makes recovery more difficult. As the body loses essential fluids due to the vomiting and inability to maintain hydration, the risk of further health issues increases, necessitating careful monitoring and management of the symptoms.
6. Altered Mental Status
In certain situations, meningitis has the potential to lead to meningitis symptoms in adults such as confusion, challenges with maintaining focus and concentration, or even alterations in a person’s level of consciousness. These effects can develop rapidly and may worsen over a short period, highlighting the importance of seeking immediate medical attention in order to address the potentially serious implications of these symptoms. It is vital that individuals experiencing such signs act swiftly, as timely intervention can be crucial for their health and well-being.
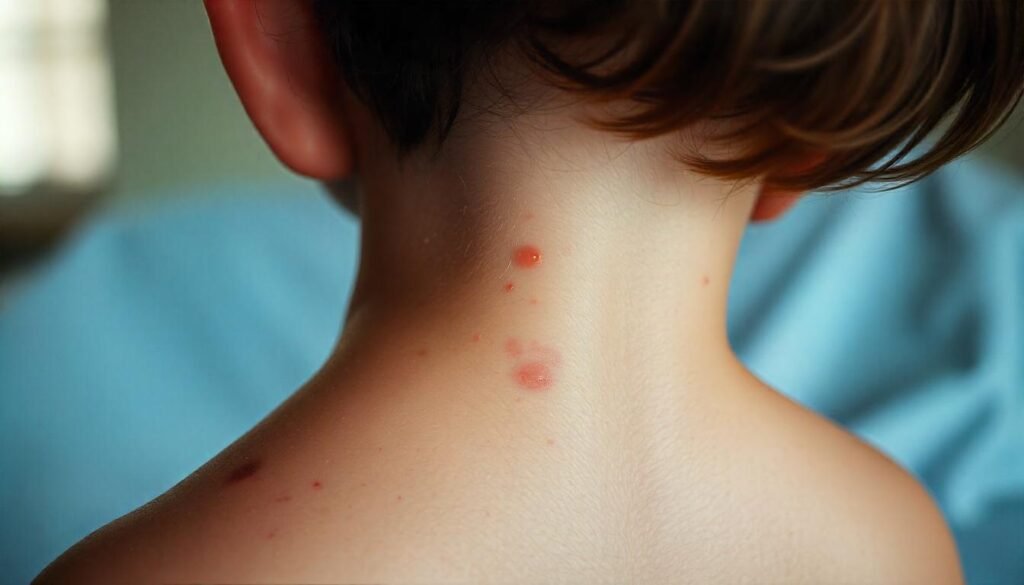
7. Rash
Certain kinds of bacterial meningitis, with a particular emphasis on meningococcal meningitis, have the potential to result in a very distinctive and alarming rash. This specific rash often manifests as small spots that are red or purple in color, and it is important to note that these spots do not fade when pressure is applied. This lack of fading is a significant indicator and can be a crucial warning sign for those affected by this serious medical condition. It is essential to monitor for meningitis symptoms in adults closely, as they may signify a severe underlying issue that requires immediate medical attention.
8. Seizures
In severe instances of the infection, individuals may experience seizures as a serious symptom. The occurrence of these seizures suggests that the infection is having a detrimental effect on brain function, which is a significant concern and indicates the need for immediate and urgent medical attention. It is crucial that anyone exhibiting such meningitis symptoms in adults seeks help promptly to address the potentially life-threatening complications associated with the infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you or someone you know exhibits several of these meningitis symptoms in adults, especially fever, severe headache, and stiff neck, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Risk Factors for Meningitis
Understanding the risk factors can help in prevention and early detection. Some common risk factors include:
Age:
- Young Adults: Individuals in the late teens and early twenties, especially those living in close proximity, such as college students in dormitories, are more susceptible to meningococcal meningitis. This age group’s social interactions and increased exposure to respiratory droplets can contribute to the rapid spread of the bacteria.
Weakened Immune System:
- Compromised Immunity: People with weakened immune systems, whether due to underlying medical conditions, medications, or recent illnesses, are at higher risk of developing meningitis. This includes individuals with HIV/AIDS, cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, and those with autoimmune disorders.

Travel:
- Geographic Variation: The prevalence of various types of meningitis is not uniform and varies significantly across different regions of the world. For instance, meningococcal meningitis is notably more prevalent and poses a greater risk in specific areas of Africa and Asia, where environmental, cultural, and health system factors may contribute to higher incidence rates. This variation highlights the need for targeted public health strategies in different geographic locations to address the unique challenges posed by these diseases.
- Pilgrimages and Group Travel: Large gatherings of individuals from a multitude of geographic locations, such as those that occur during religious pilgrimages or international travel events, can substantially elevate the risk of exposure to and the subsequent transmission of pathogens that are known to cause meningitis. Such events often involve close physical proximity among participants, which can facilitate the spread of infectious agents. Furthermore, the movement of people from regions with differing epidemiological profiles can lead to the introduction of new strains of meningitis-causing bacteria into areas where they were previously rare or non-existent, thereby complicating public health responses and increasing the overall risk to populations.

Living Conditions:
- Crowded Environments: Residing in densely populated settings, such as dormitories where students live in close quarters, military barracks where service members are housed together, or refugee camps that accommodate large groups of individuals seeking safety, can significantly enhance the likelihood of respiratory droplets that carry meningitis-causing bacteria spreading from one person to another. The close proximity of individuals in these environments creates ideal conditions for the transmission of these pathogens, which can be particularly concerning in situations where personal hygiene practices may be limited or where individuals may already be experiencing compromised health.
- Poor Ventilation: The presence of inadequate ventilation in indoor environments plays a crucial role in elevating the concentration of airborne pathogens that can linger in the air. Spaces with insufficient airflow not only allow these harmful microorganisms, including those responsible for meningitis, to accumulate to higher levels but also reduce the effectiveness of processes that normally help to disperse and dilute these particles. This lack of proper ventilation can pose a serious health risk, particularly in crowded or communal living situations where people are in close contact with one another and may inadvertently exchange respiratory droplets that contain pathogens.

Other Risk Factors:
- Recent Viral Illness: Experiencing a recent viral illness, such as the flu, can significantly weaken the immune system, leaving an individual in a more vulnerable state when it comes to combating other types of infections. This weakened immune response heightens the risk of developing bacterial infections, including serious conditions like meningitis. When the body is still recovering from a viral infection, its ability to fend off additional pathogens is compromised, making it crucial for individuals to be aware of this increased susceptibility during their recovery phase.
- Certain Medical Procedures: Medical procedures that involve direct intervention with the spinal cord or brain, including spinal taps or various forms of neurosurgery, can pose a heightened risk of meningitis if strict adherence to proper sterile techniques is not rigorously observed. These procedures create potential entry points for bacteria, and any lapse in sterilization or aseptic practices can lead to serious complications, such as infection. It is therefore essential for healthcare professionals to ensure that all protocols for cleanliness and sterility are meticulously followed to minimize the risk of developing infections like meningitis following such delicate medical interventions.
Prevention Strategies
While not all forms of meningitis are preventable, there are several strategies that can help reduce the risk:
1. Vaccination
Vaccines are currently available for a variety of types of bacterial meningitis, which is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection. It is essential for individuals, particularly college students and frequent travelers, to stay up-to-date with their vaccinations. By doing so, they can gain significant protection against these infections, reducing their risk of contracting meningitis during their activities. Being proactive about vaccinations not only safeguards personal health but also contributes to the well-being of the broader community.
2. Good Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene practices, which include regular handwashing and making a conscious effort to avoid sharing personal items with others, can significantly contribute to the prevention of the spread of infections. By consistently washing your hands with soap and water, especially after using the restroom or before eating, you can effectively eliminate germs that may cause illness. Additionally, being mindful about not passing along items such as towels, utensils, or personal care products is crucial in reducing the likelihood of transmitting harmful pathogens.
3. Awareness of Meningitis Symptoms in Adults
Having a clear understanding of the various meningitis symptoms in adults that may arise and responding promptly can significantly increase the chances of receiving timely medical intervention. This quick action is essential, as it plays a crucial role in ensuring a better outcome for the individual affected. Recognizing the signs early and taking appropriate steps can make all the difference in the effectiveness of the treatment received.
Conclusion
Understanding the meningitis symptoms in adults is vital for early detection and treatment. The combination of fever, severe headache, stiff neck, and altered mental status should prompt immediate medical attention. By recognizing these signs and taking preventive measures, individuals can protect themselves and their loved ones from this potentially life-threatening condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What should I do if I think I have meningitis?
A1: If you have any reason to believe that you may have meningitis, it is essential to seek medical attention right away. Obtaining a timely diagnosis and receiving prompt treatment are vital components in managing this potentially serious condition effectively.
Q2: Can meningitis be treated?
A2: Absolutely, bacterial meningitis is a condition that can be effectively treated with antibiotics, which are essential in combating the bacterial infection that causes this serious illness. On the other hand, viral meningitis usually resolves naturally, as the body’s immune system is often capable of overcoming the viral infection without the need for specific antiviral therapies. It is important to note, however, that regardless of the type of meningitis—bacterial or viral—both conditions necessitate prompt medical evaluation to ensure proper diagnosis and management.
Q3: Are there vaccines for meningitis?
A3: Indeed, there are multiple vaccines available that can offer protection against various strains of bacterial meningitis. It is important to engage in a conversation with your healthcare provider to receive personalized recommendations based on your specific health needs and circumstances.
Q4: How can I prevent meningitis?
A4: Vaccination against the disease, along with the implementation of good hygiene practices and a thorough awareness of the meningitis symptoms in adults that may arise, can significantly contribute to the prevention of meningitis. By taking these important steps, individuals can effectively reduce their risk of contracting this serious condition.
Q5: What are the long-term effects of meningitis?
A5: Certain individuals may experience a range of long-term effects that can significantly impact their daily lives. These effects may include, but are not limited to, hearing loss, difficulties with learning, or various neurological issues. This is especially true for those who do not receive timely treatment, as delays in addressing these conditions can exacerbate their severity and lead to more complex challenges over time.
By prioritizing awareness and education about meningitis symptoms in adults, we can empower individuals to take control of their health and seek timely medical care when necessary.



